HSE Neurolinguists Reveal What Makes Apps Effective for Aphasia Rehabilitation
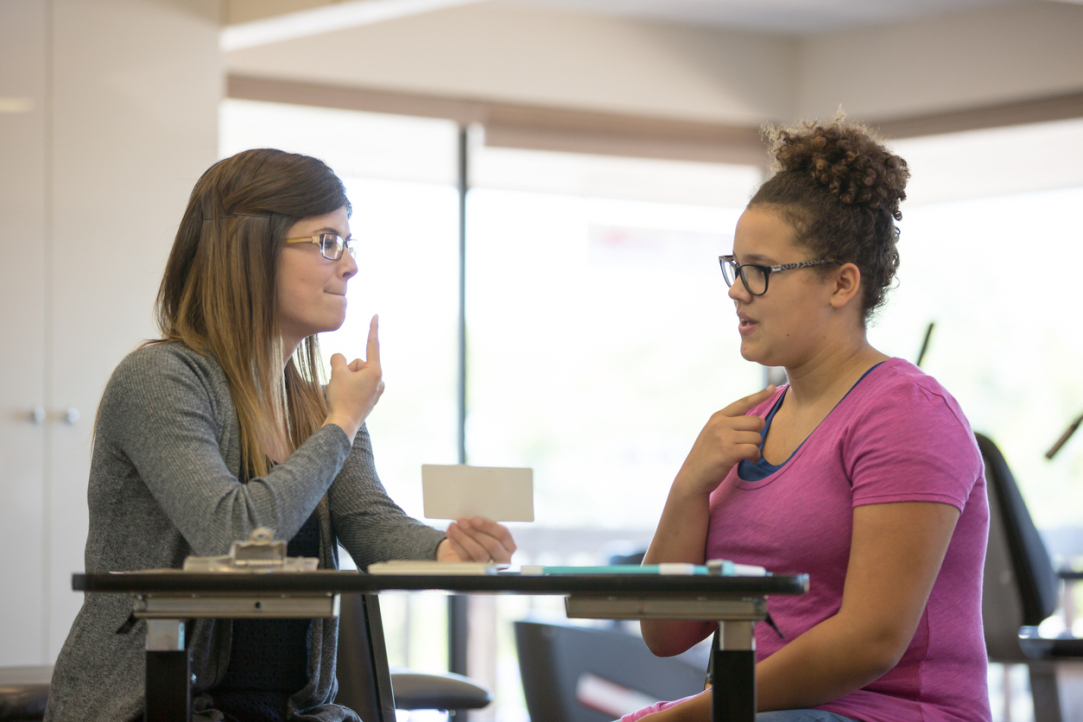

Scientists at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have identified key factors that increase the effectiveness of mobile and computer-based applications for aphasia rehabilitation. These key factors include automated feedback, a variety of tasks within the application, extended treatment duration, and ongoing interaction between the user and the clinician. The article has been published in NeuroRehabilitation.
Aphasia is a disorder characterised by complete or partial loss of the ability to speak and understand speech, caused by damage to areas of the brain responsible for language functions. The primary causes of aphasia include stroke, traumatic brain injury, inflammatory brain diseases, brain tumours, and dementia.
Aphasia significantly reduces a person's quality of life, prompting scientists to search for effective ways to restore the language functions impaired by the condition. With the widespread use of smartphones and tablets, a promising and rapidly evolving area of rehabilitation has emerged: serious games (SG) integrated into applications.
These are a special type of digital game designed not only for entertainment, but also to serve specific educational, training, or research purposes. In education, they support professional training, student learning, and foreign language acquisition. In healthcare, such games are used for patient rehabilitation.
Using a specially designed application, a person with aphasia can complete language training tasks and gradually recover their lost abilities. The effectiveness of such applications has already been demonstrated, but it remained unclear which specific tasks and features should be included, and how long users should engage with them to achieve optimal results.
Scientists from the HSE Centre for Language and Brain searched the PubMed and ScienceDirect databases and selected 18 studies which tested mobile and computer applications for aphasia rehabilitation.
The researchers focused specifically on cases where using an application produced remarkable results. For example, a patient who practiced naming 100 words improved to naming 150 words or was able to use the learned words not only in speech but also in writing. Sometimes, using serious games led to the development of related skills; for example, while training language functions, a person’s attention also improved.
In 14 of the 18 papers analysed (78%), patient use of the application resulted in positive effects. While most studies confirmed the effectiveness of the applications based on primary outcomes—ie improvement in the specific skills being trained—eight articles (44%) reported results that exceeded expectations, often showing that patients could apply the trained words in other contexts, such as writing. Additionally, two studies reported improvements in other higher cognitive functions.
The analysis revealed that the effectiveness of the applications was influenced by factors such as automated feedback, a diverse range of training tasks, extended treatment duration, and interaction between the patient and clinician. The latter is particularly important, as clinicians provide additional motivation and assess interim progress.
'At our centre, we are developing a game for aphasia rehabilitation. Reviewing existing studies will help us optimise its testing and incorporate the essential features needed for effective use. Many existing applications include few gamification elements and function more like digital workbooks with exercises. We aim to address this limitation to increase user engagement,' explains Georgii Gorshkov, Junior Research Fellow at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain.
The study was conducted with support from the Government of Moscow (Grant No. 1403-18/23).
See also:
Mathematician from HSE University–Nizhny Novgorod Solves Equation Considered Unsolvable in Quadratures Since 19th Century
Mathematician Ivan Remizov from HSE University–Nizhny Novgorod and the Institute for Information Transmission Problems of the Russian Academy of Sciences has made a conceptual breakthrough in the theory of differential equations. He has derived a universal formula for solving problems that had been considered unsolvable in quadratures for more than 190 years. This result fundamentally reshapes one of the oldest areas of mathematics and has potential to have important implications for fundamental physics and economics. The paper has been published in Vladikavkaz Mathematical Journal.
Scientists Reveal How Language Supports Complex Cognitive Processing in the Brain
Valeria Vinogradova, a researcher at HSE University, together with British colleagues, studied how language proficiency affects cognitive processing in deaf adults. The study showed that higher language proficiency—regardless of whether the language is signed or spoken—is associated with higher activity and stronger functional connectivity within the brain network responsible for cognitive task performance. The findings have been published in Cerebral Cortex.
HSE AI Research Centre Simplifies Particle Physics Experiments
Scientists at the HSE AI Research Centre have developed a novel approach to determining robustness in deep learning models. Their method works eight times faster than an exhaustive model search and significantly reduces the need for manual verification. It can be applied to particle physics problems using neural networks of various architectures. The study has been published in IEEE Access.
Scientists Show That Peer Influence Can Be as Effective as Expert Advice
Eating habits can be shaped not only by the authority of medical experts but also through ordinary conversations among friends. Researchers at HSE University have shown that advice from peers to reduce sugar consumption is just as effective as advice from experts. The study's findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE University Develops Tool for Assessing Text Complexity in Low-Resource Languages
Researchers at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed a tool for assessing text complexity in low-resource languages. The first version supports several of Russia’s minority languages, including Adyghe, Bashkir, Buryat, Tatar, Ossetian, and Udmurt. This is the first tool of its kind designed specifically for these languages, taking into account their unique morphological and lexical features.
HSE Scientists Uncover How Authoritativeness Shapes Trust
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have studied how the brain responds to audio deepfakes—realistic fake speech recordings created using AI. The study shows that people tend to trust the current opinion of an authoritative speaker even when new statements contradict the speaker’s previous position. This effect also occurs when the statement conflicts with the listener’s internal attitudes. The research has been published in the journal NeuroImage.
Language Mapping in the Operating Room: HSE Neurolinguists Assist Surgeons in Complex Brain Surgery
Researchers from the HSE Center for Language and Brain took part in brain surgery on a patient who had been seriously wounded in the SMO. A shell fragment approximately five centimetres long entered through the eye socket, penetrated the cranial cavity, and became lodged in the brain, piercing the temporal lobe responsible for language. Surgeons at the Burdenko Main Military Clinical Hospital removed the foreign object while the patient remained conscious. During the operation, neurolinguists conducted language tests to ensure that language function was preserved.
AI Overestimates How Smart People Are, According to HSE Economists
Scientists at HSE University have found that current AI models, including ChatGPT and Claude, tend to overestimate the rationality of their human opponents—whether first-year undergraduate students or experienced scientists—in strategic thinking games, such as the Keynesian beauty contest. While these models attempt to predict human behaviour, they often end up playing 'too smart' and losing because they assume a higher level of logic in people than is actually present. The study has been published in the Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization.
Scientists Discover One of the Longest-Lasting Cases of COVID-19
An international team, including researchers from HSE University, examined an unusual SARS-CoV-2 sample obtained from an HIV-positive patient. Genetic analysis revealed multiple mutations and showed that the virus had been evolving inside the patient’s body for two years. This finding supports the theory that the virus can persist in individuals for years, gradually accumulate mutations, and eventually spill back into the population. The study's findings have been published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.
HSE Scientists Use MEG for Precise Language Mapping in the Brain
Scientists at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have demonstrated a more accurate way to identify the boundaries of language regions in the brain. They used magnetoencephalography (MEG) together with a sentence-completion task, which activates language areas and reveals their functioning in real time. This approach can help clinicians plan surgeries more effectively and improve diagnostic accuracy in cases where fMRI is not the optimal method. The study has been published in the European Journal of Neuroscience.