Mathematicians from HSE University–Nizhny Novgorod Solve 57-Year-Old Problem
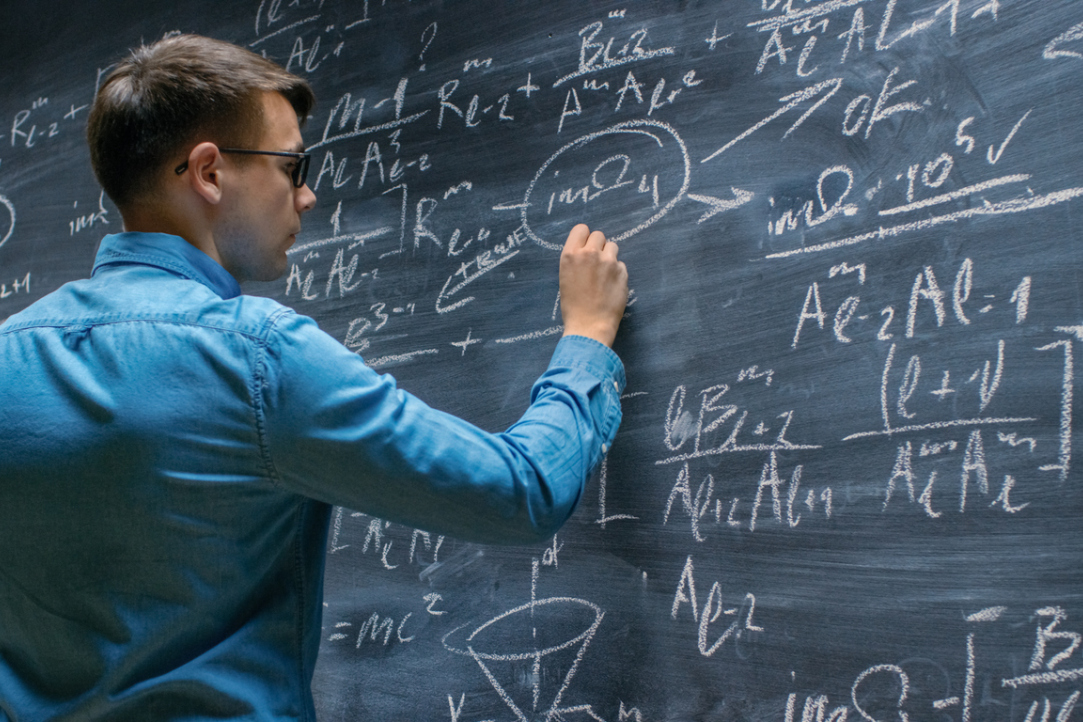
In 1968, American mathematician Paul Chernoff proposed a theorem that allows for the approximate calculation of operator semigroups, complex but useful mathematical constructions that describe how the states of multiparticle systems change over time. The method is based on a sequence of approximations—steps which make the result increasingly accurate. But until now it was unclear how quickly these steps lead to the result and what exactly influences this speed. This problem has been fully solved for the first time by mathematicians Oleg Galkin and Ivan Remizov from the Nizhny Novgorod campus of HSE University. Their work paves the way for more reliable calculations in various fields of science. The results were published in the Israel Journal of Mathematics (Q1).
Many mathematical and theoretical physics problems require precise calculations of complex specific values, such as how quickly a cup of coffee cools down, how heat spreads in an engine, or how a quantum particle behaves. Research into quantum computers and quantum information transmission channels, random processes, and many other areas important to modern science involve calculating semigroups of operators. Such calculations are based on the exponent, one of the most important mathematical functions expressed by the number e (approximately equal to 2.718) raised to a power.
However, in the case of very complex systems described by so-called unbounded operators, standard methods for calculating the exponent (semigroup of operators) stop working. In 1968, American mathematician Paul Chernoff proposed an elegant solution to this problem: a special mathematical approach now known as Chernoff approximations of semigroups of operators. This makes it possible to approximately calculate the required values of the exponent by consistently building more and more precise mathematical constructions.
Chernoff's method guaranteed that successive approximations would eventually lead to the correct answer, but did not show how quickly this would happen. Simply put, it was unclear how many steps were needed to achieve the desired accuracy. It was this uncertainty that prevented the method from being used in practice.
Mathematicians Oleg Galkin and Ivan Remizov from HSE University–Nizhny Novgorod solved this problem, which scientists around the world had struggled with for many decades. They managed to obtain general estimates of the convergence rate—that is, to describe how quickly the approximate values converge to the exact result depending on the selected parameters.

Ivan Remizov
‘This situation can be compared to a culinary recipe. Paul Chernoff indicated the necessary stages, but did not explain how exactly to select the optimal "ingredients"—auxiliary Chernoff functions that provide the best result. Therefore, it was impossible to accurately predict how quickly the “dish” would be ready. We have refined this recipe and determined which ingredients are best suited to make the method faster and more efficient,’ explains Ivan Remizov, senior researcher at the HSE International Laboratory of Dynamical Systems and Applications, senior researcher at the RAS Dobrushin Laboratory of the A.A. Kharkevich Institute for Information Transmission Problems, and co-author of the study.
Galkin and Remizov showed that Chernoff’s method can work much faster if the auxiliary Chernoff functions are chosen correctly. With the right selection of functions, the approximation becomes much more accurate even at the early stages of calculations. The mathematicians also proved a rigorous theorem: if the Chernoff function and the semigroup being approximated have the same Taylor polynomial of order k, and the Chernoff function deviates little from its Taylor polynomial, then the difference between the approximate and exact values decreases at least proportionally to 1/n^k, where n is the step number and k is any natural number reflecting the quality of the selected functions.

Oleg Galkin
Continuing the recipe analogy, the scientists have managed not only to clarify which ingredients work best, but also to accurately estimate how much faster the ‘dish’ is prepared if these optimal products are used. The formula derived by the mathematicians based on this analogy works like this: at each step of preparation, the result becomes more accurate, and the error decreases proportionally to one divided by n to the power of k, where n denotes the step number in the recipe, and k depends on the quality of the selected ingredients. The higher the value of k, the faster the desired result will be achieved.
Thus, Oleg Galkin and Ivan Remizov managed to solve a problem that had remained open for more than half a century. In addition to bringing clarity, their achievement could open up prospects and generate new problems to be solved. Although the study is theoretical in nature, its significance goes beyond pure mathematics. Such results often serve as the basis for developing new numerical methods in quantum mechanics, heat transfer, control theory, and other sciences where complex processes are modeled.
The theorem proposed by Oleg Galkin and Ivan Remizov was presented at the international scientific conference ‘Theory of Functions and Its Applications’ on July 5, 2025.
The work was supported by the HSE Fundamental Research Programme and the HSE International Laboratory of Dynamical Systems and Applications, grant No. 23-71-30008 of the Russian Science Foundation ‘Dissipative Dynamics of Infinite-Dimensional and Finite-Dimensional Systems, Development of Mathematical Models of Mechanical and Hydrodynamic Processes.’
See also:
HSE AI Research Centre Simplifies Particle Physics Experiments
Scientists at the HSE AI Research Centre have developed a novel approach to determining robustness in deep learning models. Their method works eight times faster than an exhaustive model search and significantly reduces the need for manual verification. It can be applied to particle physics problems using neural networks of various architectures. The study has been published in IEEE Access.
Scientists Show That Peer Influence Can Be as Effective as Expert Advice
Eating habits can be shaped not only by the authority of medical experts but also through ordinary conversations among friends. Researchers at HSE University have shown that advice from peers to reduce sugar consumption is just as effective as advice from experts. The study's findings have been published in Frontiers in Nutrition.
HSE University to Host Second ‘Genetics and the Heart’ Congress
HSE University, the National Research League of Cardiac Genetics, and the Central State Medical Academy of the Administrative Directorate of the President will hold the Second ‘Genetics and the Heart’ Congress with international participation. The event will take place on February 7–8, 2026, at the HSE University Cultural Centre.
HSE University Develops Tool for Assessing Text Complexity in Low-Resource Languages
Researchers at the HSE Centre for Language and Brain have developed a tool for assessing text complexity in low-resource languages. The first version supports several of Russia’s minority languages, including Adyghe, Bashkir, Buryat, Tatar, Ossetian, and Udmurt. This is the first tool of its kind designed specifically for these languages, taking into account their unique morphological and lexical features.
HSE Scientists Uncover How Authoritativeness Shapes Trust
Researchers at the HSE Institute for Cognitive Neuroscience have studied how the brain responds to audio deepfakes—realistic fake speech recordings created using AI. The study shows that people tend to trust the current opinion of an authoritative speaker even when new statements contradict the speaker’s previous position. This effect also occurs when the statement conflicts with the listener’s internal attitudes. The research has been published in the journal NeuroImage.
Language Mapping in the Operating Room: HSE Neurolinguists Assist Surgeons in Complex Brain Surgery
Researchers from the HSE Center for Language and Brain took part in brain surgery on a patient who had been seriously wounded in the SMO. A shell fragment approximately five centimetres long entered through the eye socket, penetrated the cranial cavity, and became lodged in the brain, piercing the temporal lobe responsible for language. Surgeons at the Burdenko Main Military Clinical Hospital removed the foreign object while the patient remained conscious. During the operation, neurolinguists conducted language tests to ensure that language function was preserved.
HSE MIEM and AlphaCHIP Innovation Centre Sign Cooperation Agreement
The key objectives of the partnership include joint projects in microelectronics and the involvement of company specialists in supervising the research activities of undergraduate and postgraduate students. Plans also focus on the preparation of joint academic publications, the organisation of industrial placements and student internships, and professional development programmes for the company’s specialists.
AI Overestimates How Smart People Are, According to HSE Economists
Scientists at HSE University have found that current AI models, including ChatGPT and Claude, tend to overestimate the rationality of their human opponents—whether first-year undergraduate students or experienced scientists—in strategic thinking games, such as the Keynesian beauty contest. While these models attempt to predict human behaviour, they often end up playing 'too smart' and losing because they assume a higher level of logic in people than is actually present. The study has been published in the Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization.
HSE University and InfoWatch Group Sign Cooperation Agreement
HSE University and the InfoWatch Group of Companies marked the start of a new stage in their collaboration with the signing of a new agreement. The partnership aims to develop educational programmes and strengthen the practical training of specialists for the digital economy. The parties will cooperate in developing and reviewing curricula, and experts from InfoWatch will be involved in teaching and mentoring IT and information security specialists at HSE University.
Scientists Discover One of the Longest-Lasting Cases of COVID-19
An international team, including researchers from HSE University, examined an unusual SARS-CoV-2 sample obtained from an HIV-positive patient. Genetic analysis revealed multiple mutations and showed that the virus had been evolving inside the patient’s body for two years. This finding supports the theory that the virus can persist in individuals for years, gradually accumulate mutations, and eventually spill back into the population. The study's findings have been published in Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology.